
Exchange Server 2013 is an iteration of Microsoft’s Exchange server. Exchange Server 2013 is similar to Exchange Server 2010 in that the messaging platform can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud or as a hybrid solution in which some servers exist on-premises while others reside in the cloud.
There are few things you should be aware of before you start working with Exchange 2013.
- Exchange 2013 system requirements
- Exchange 2013 prerequisites
- Prepare Active Directory and domains
- Install Exchange 2013 using the Setup wizard
- Install Exchange 2013 using unattended mode
- Exchange 2013 post-Installation tasks
- Exchange Migration
Exchange Server 2013 Architecture Poster
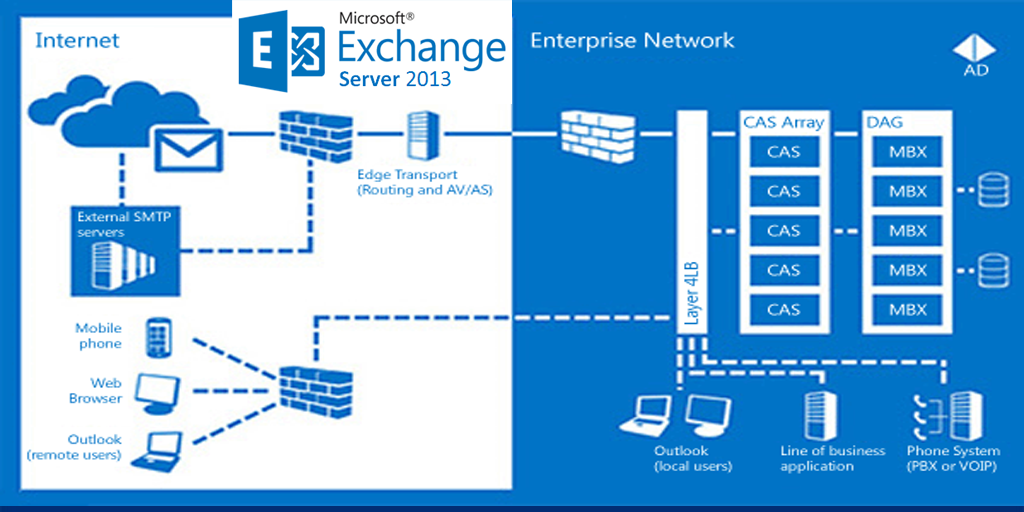
Associated Server Roles
There are 2 associated server roles you can install in single or multi servers.
| 1 | CAS | Client Access | OWA / POP / IMAP / Active sing / Outlook any way ware |
| 2 | MB | Mailbox | Store Mail Box / Public folder / Calendrer / Contacts |
Exchange 2013 licensing
- Exchange 2013 Standard edition. Supports up to a total of 5 mailbox databases per server.
- Exchange 2013 Enterprise edition. Supports up to a total of 50 mailbox databases per server.
Exchange 2013 New Features
Here’s a list from Microsoft of some of the new Exchange Server 2013 features:
- Outlook Web App (OWA) Access your email, calendars, and contacts from anywhere on any device using Web Apps in the browser. Outlook Web App offers three different layouts optimized for PCs, smartphones, and tablets with a touch-friendly interface.
- Offline support in OWA Emails and actions are automatically synced the next time connectivity is restored.
- Site Mailboxes and In-Place eDiscovery Brings Exchange emails and SharePoint documents together. Improved integration with both SharePoint and Lync.
- Customization Outlook and OWA can now be customized with apps from the Office marketplace.
- Exchange Administrative Center (EAC) The old Exchange Management Console has been replaced by the Web-based Exchange Administrative Center (EAC).
- Support for larger disk sizes Up to 8TB disks and multiple databases per disk via Data Availability Group (DAG) management.
- Built in anti-malware protection Administrators have the ability to configure and manage settings for malware protection from inside EAC.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) New capabilities for identifying and protecting “sensitive data.” DLP policies are based on regulatory standards, including PII and PCI. In addition, new policy tips in Outlook 2013 can be set to inform users about potential policy violations.
- Combined Roles A reduction in the number of available roles to two: a Client Access Server and a Mailbox Server role.
- FAST Search Now integrated into Exchange 2013 managed store to provide a more consistent indexing and searching experience across Microsoft servers.
- Inclusion of a “Managed Store” Information store processes, rewritten in C#.
- Replication Public folders are now stored in mailbox databases and can take advantage of Database Availability Groups for replication and high availability.
- Data loss prevention Capabilities that can be integrated into Transport Rules.