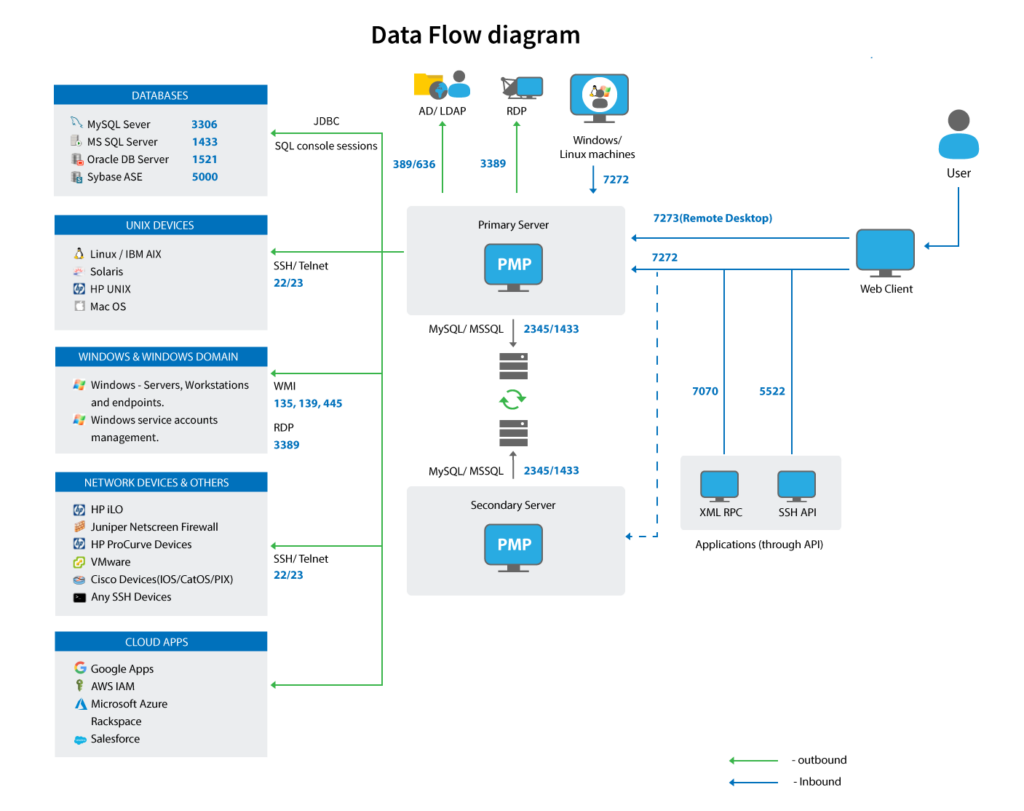
To get started with Password Manager Pro (PMP), a secure solution for managing passwords and sensitive information, here are some basic configurations and best practices to consider:
1. User Roles and Permissions
- Admin: Grant access to the system settings and user management features.
- User: Allow limited access to their own passwords and shared credentials.
- Super Admin: Configure system-wide settings, manage roles, and set up policies.
- Read-Only: Restrict users to only view passwords without modification rights.
Best Practice: Define roles clearly to minimize exposure and ensure only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
2. Password Storage
- Set up Password Vaults to organize your passwords by departments, groups, or projects.
- Enable Password Security settings (e.g., password length, complexity rules) to enforce strong passwords.
- Configure Password Retention Policies for how long passwords should be retained in the vault.
3. Authentication
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Configure MFA to enhance the security of accounts, especially for admins or users accessing sensitive passwords.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Enable SSO for integration with identity providers to simplify the authentication process.
4. Password Sharing and Access
- Password Sharing: Set rules for securely sharing passwords among team members with granular permissions (view, edit, share).
- Access Control: Limit access to certain passwords or vaults for specific users or roles.
5. Password Rotation and Auditing
- Enable Password Rotation policies for automated password changes at specified intervals.
- Set up Audit Logs to track changes to passwords, access logs, and system configurations for compliance and security monitoring.
6. Emergency Access
- Set up an Emergency Access policy to define who can access critical passwords or systems in case of an emergency (e.g., authorized personnel or management).
7. Integration with Other Tools
- Directory Integration: Integrate PMP with your corporate directory service (like LDAP or Active Directory) for user management.
- SIEM Integration: Integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to centralize security event logging.
8. Backup and Recovery
- Set up Backup procedures for password data to ensure data integrity and availability in case of a disaster or system failure.
- Ensure that you have a Recovery Plan for restoring data and system configurations.
9. Email Notifications
- Configure email alerts for password changes, new password sharing requests, and security-related actions.
- Set thresholds for when notifications should be triggered (e.g., failed login attempts or password expiry).
10. Compliance and Reporting
- Configure reporting to meet compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or other regulatory frameworks.
- Set up regular reports on password usage, access control, and compliance.
Example Basic Configuration Steps to Get Started:
- Set up Users and Groups: Create user roles like Admin, User, and Reader. Organize users into groups (e.g., marketing, IT, etc.).
- Configure Password Vaults: Create different vaults for departments or projects (e.g., “Marketing Vault”, “Admin Vault”).
- Enable MFA for all users, especially admins.
- Define Password Policies: Set up minimum password strength requirements (e.g., 12 characters, must include special characters).
- Set Password Rotation policies to rotate passwords every 30/60/90 days.
- Configure Audit Logging: Enable detailed auditing for monitoring access and changes.
- Enable Backup: Set up regular backups to ensure password data is protected.
Once these basic configurations are set up, you can expand on them based on your organization’s needs and security policies.